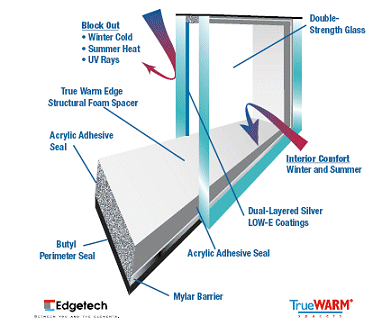
Insulated glazing (IG) also known as double glazing are double or triple glass window panes separated by an air or other gas filled space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope.
Glass in windows is used to provide light and allow a view from either side to the other side. While the composition and manufacturing of glass is covered elsewhere, for the purposes of this article, its importance to the construction is its dimensional stability over a wide temperature range.
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) are manufactured with glass in range of thickness from 3 mm to 10 mm or more in special applications. Laminated or tempered glass may also be used as part of the construction. Most units are manufactured with the same thickness of glass used on both panes but special applications such as acoustic attenuation or security may require wide ranges of thicknesses to be incorporated in the same unit.
The heat loss of a window can be estimated by calculation. Given the thermal properties of the sash, frame, and sill, and the dimensions of the glazing and thermal resistance of the glass, the heat transfer can be calculated.
The life of an IGU varies depending on the quality of materials used, size of gap between inner and outer pane, temperature differences, workmanship and location of installation both in terms of facing direction and geographic location. IG units typically last from 10 to 25 years, with windows facing south (Northern Hemisphere) or the north (Southern Hemisphere) often lasting less than 12 years. IGUs typically carry a warranty for 10 to 20 years depending upon the manufacturer. If IGUs are altered (such as installation of a solar control film) the warranty may be voided by the manufacturer.
